Why GES or Can We Reduce Extensive Work Experience to a Simple Score?
Why GES or Can We Reduce Extensive Work Experience to a Simple Score?

Our goal is to answer a simple question any job seeker is asking, which is what are my chances to find a better position in the company I work for, or in another one? We also want to wrap that answer in a simple score that can be used as a guideline, or target, regardless of the size of the paycheck, titles, or company field. To be able to do that we are using a sophisticated model that describes how all businesses are operating, regardless of the size, field, products, strategy, or even the country they operate.
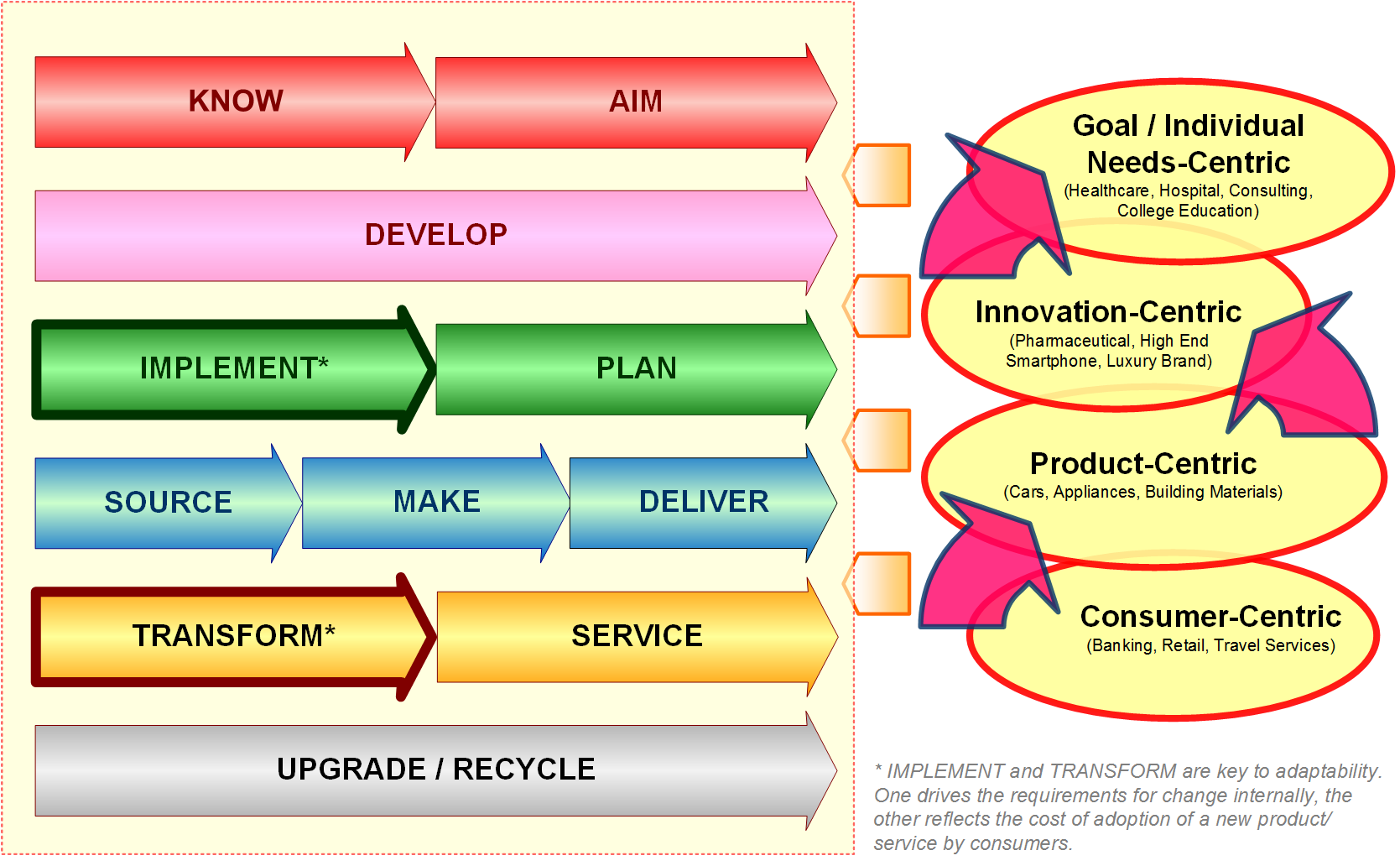
The next section shows a panel that allows you to navigate our model. It also shows various how various areas of business are split based on complexity, role, cycle. The end result for a job candidate is a graphical resume, which captures in a single diagram the entire work experience. Because the way various business functions are related in a business, with each job role and grade associated, our assessemnt methodology can also provide guidelines on recommended what further skills and education a job seeker needs to pursue, and what would be the next best option for a given career target.
To note that GES (Gainful Employment Score) can be easier to calculate for college graduates working in businesses medium-size and higher. There are two main reasons for this. First, significant gains in skills and opportunities to learn mainly applies to college graduates. Second, only businesses of a certain size are organized around an internal structure which distinguishes clearly between various basic functions. The smaller the business, the more lines between different roles are usually blurred. There are also two fields - government and investment - with a different operating model which we do not cover with current approach. Later versions will address those too.
Graphical Resume and the Adaptive Enterprise Operational Platform (AEOP)
Select one of the following options to display various functions, scores, and business models.
Select one of the following career path to highlight on the diagram:
Show a graphical resume for a feasible VP of Business Development career path:
Opacity
GES Score - Factors Used in Calculation
There are three main factors used in calculating GES. One is the business contex in which job seeker performs. The second is associated to the job role. And the third is related to personal achievments. The score is primarily based on the business context and not on the job seeker experience. It associates the tasks to real needs of the business.
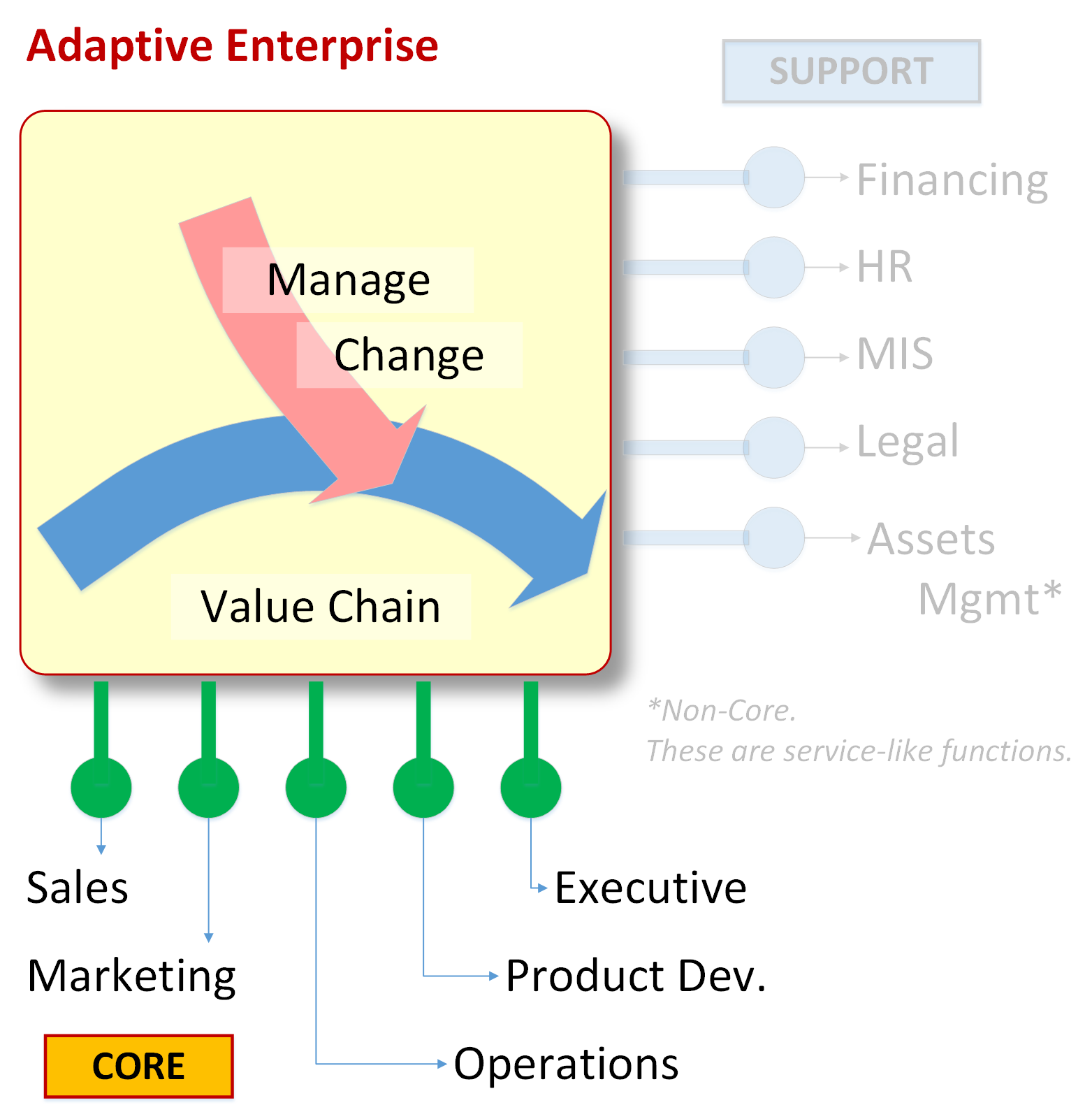
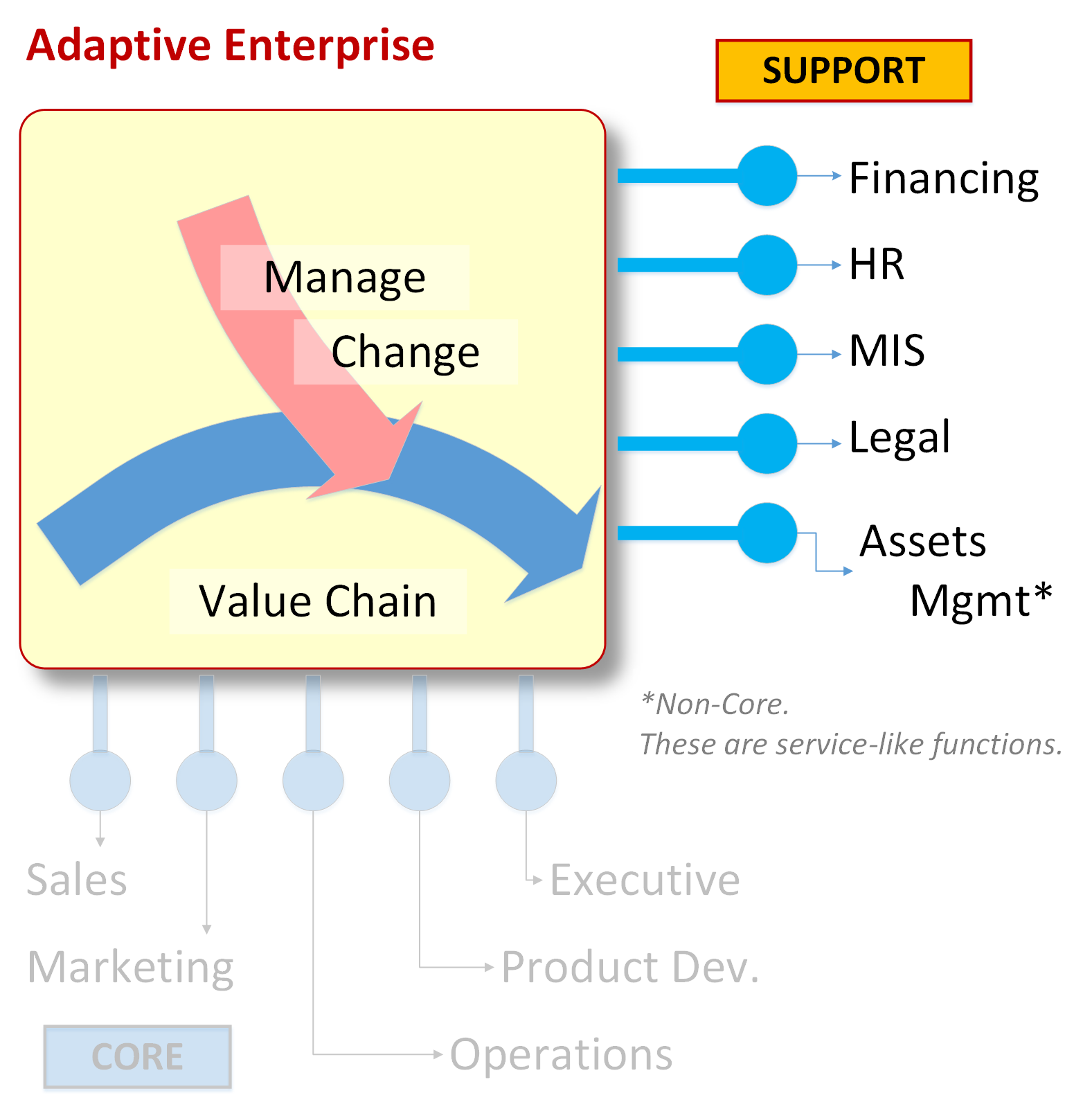
For traditional businesses, which are the vast majority of employers, all GES scores are associated with one of ten main standard career path. There are five paths found in core operations, and five in functions which provide support to the business. Paths found in core are: Operations (COO), Sales (VP of Sales), Marketing (CMO), Product Development (CTO), and Executive Leadership (CEO). Paths found in support are: Financing (CFO), Human Resources (VP of HR), Management Information Systems (CIO), Assets Management (Non-Production Assets), and Legal (Corporate Legal Counsel).
In calculating the GES for a job seeker, the most important is the job context, next job role, and last personal achievments. The closer to origin, the more important factor in calculation.
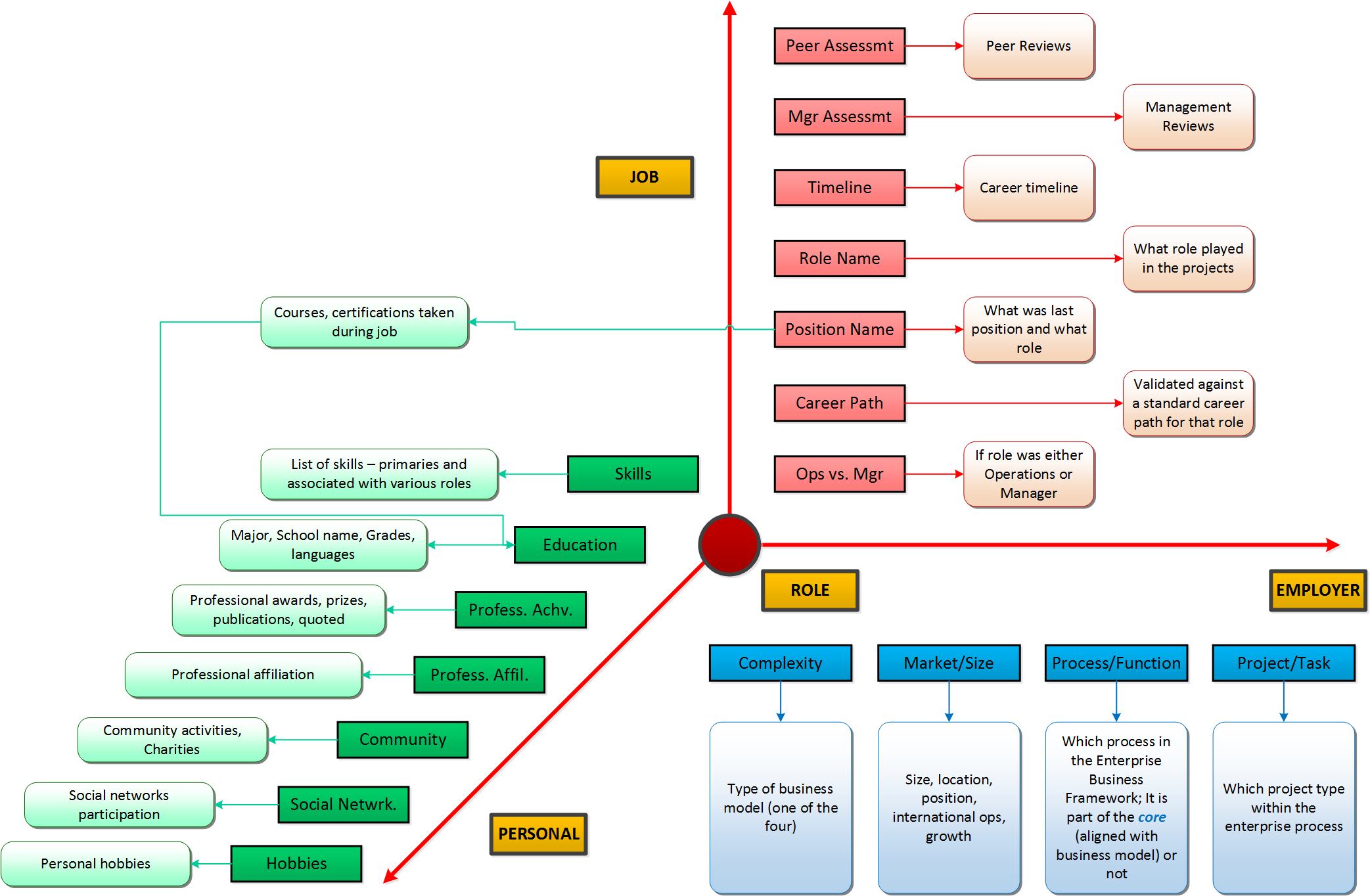
In the first phase, for each past experience, a job seeker enters the employer information first. It start with the type of business model (one out of four), then the size of the company, then the business function where the job seeker performed the tasks, and ends with the actual project name.
Employer
Complexity: Type of business model (consumer centric, product-centric, innovation-centric, goal/individual needs-centric)
Market/Size: Industry field, product cycle length, size, location, position, international operations, growth.
Process/Function: It is one of the over 100 business functions. The score is calculating primarily based on the cycle the business function is part of.
Project: For each type of business functions there are typical tasks/projects associated. A job seeker needs to select the one where he/she contributed the most.
In the next phase, a job seeker uses the tasks/projects as the starting point. The next section can have multiple entries for the same project as job seeker switches tasks/projects.
JobOperative vs. Manager: There is a fundamental distinction between a manager role or an operative one. Their contribution is captured by different values.
Career Path: This is when there is a different career goal than the one used for the overall score. It is selected from one of the ten.
Position Name: The official position name.
Role Name: The official position role description. It has to match roles found in the business function.
Timeline: For how long the job seeker contributed to the task/project.
Manager Assessment: Enter the manager review
Peer Assessments: Enter peer reviews.
In the last phase job seeker enters personal information. Same as before, the starting point is the data from the previous phase. For each task/project job seeker enters only those relevant skills and certification, degrees, etc. All personal data is evaluated against the main career path for relevance.
Personal
Skills: Enter only the relevant skills associated with tasks/projects.
Education: The closer to the selected career path, the higher the score. Added here certifications granted during work.
Professional Achievments: Professional awards, certifications, etc.
Professional Affiliations: Member of professional associations such as IEEE, APS, etc.
Community Work: Here job seeker enters participation in charity events and other community activities.
Social Network Presence: Linkedin profile, Blogs, etc.
Hobbies: Activities such as sports, languages spoken, etc.
Short Summary of GES
It does not apply to career paths in government or investing field. Our goal is to add functional models for those fields in the near future if there are enough requests.
Gainful Employment Score (GES) for Business Roles
- Definition: measures job seeker ability to cope with change (Operative) or drive change (Manager)
- Applies: job seekers from all business roles (except Information Systems)
-
Business Roles:
Operative: Entry Level, Operative, Senior Operative, Project Manager
Management: Team Lead, Manager, Departement Manager, VP, C-Level, CEO
-
Major Career Paths:
Core: Sales (VP of Sales), Marketing (CMO), Operations (COO), Product Development (CTO), Top Leader (CEO)
Support: Financing (CFO), Human Resources (VP of HR) Management Information Systems (CIO), Assets Management (Non-Core Assets such as Facilities, etc.) Legal (Corporate Legal Counsel)
- Measures: O - operative skills M - management skills
- Factors used in calculation: business context in which job role, tasks associated with job role, and personal achievements
- Values: two values - 0 to 1000
-
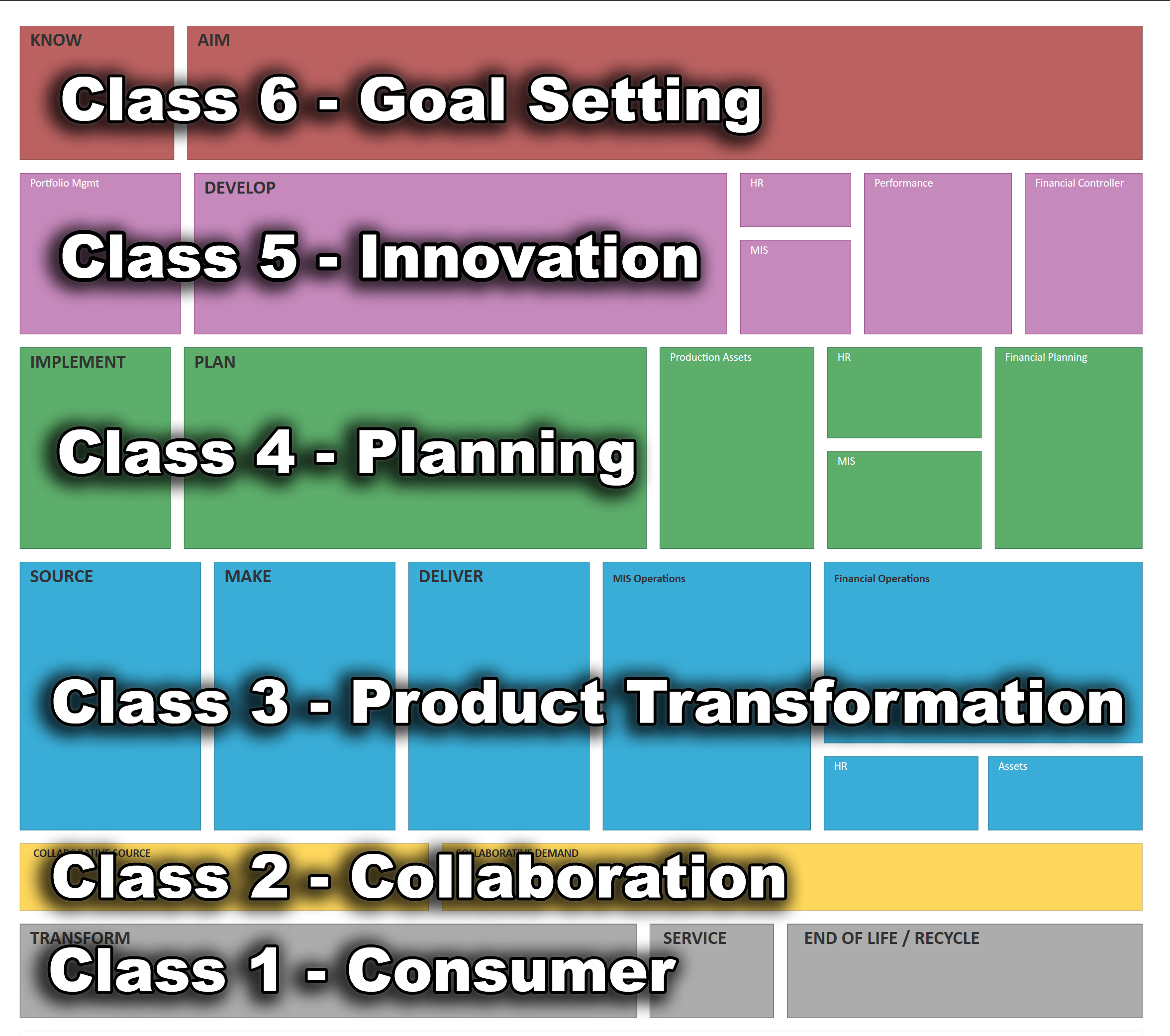
Class ratings (per business cycle):
Consumer cycle:0 to 200Product cycle:200 to 550Innovation cycle:550 to 700Goal/Individual Needs cycle:700 to 1000 -
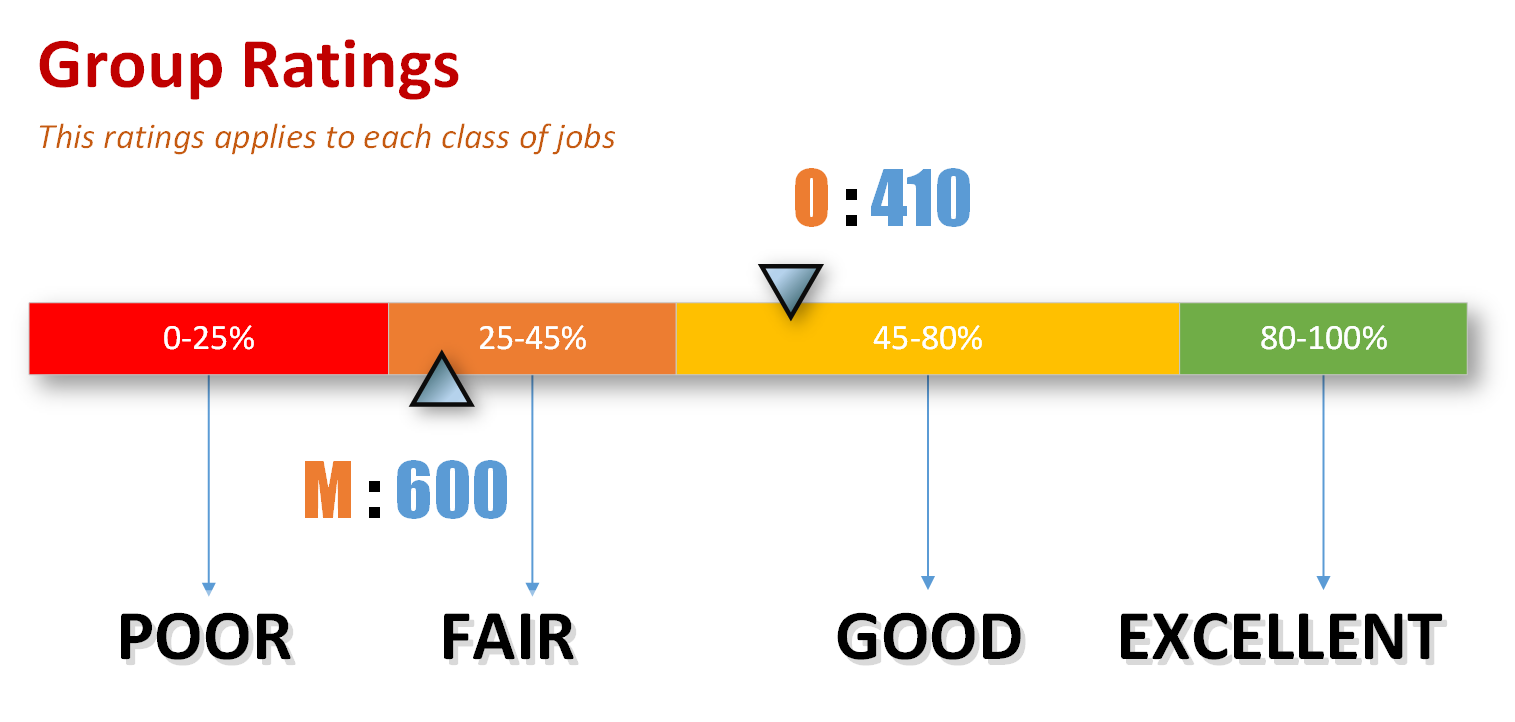
Group ratings for each class calculated as percentage:
Poor:0 to 25 %Fair:25 to 45 %Good:45 to 80 %Excellent:80 to 100 %
Score assessment: past role interact with customer, currently manager in core operations(make, deliver, source)
For an experience in a business function to be counted with maximum points, a job seeker has to participate in at least three full cycles of the main business model. For instance, in product-centric businesses, a cycle is usually counted as a main revision/update to a product. For innovation-based business model, a full cycle is usually counted as one year as most of the businesses make major updates every year. There are exceptions to this in industries such as pharma, management consulting, health care. For consumer-cycle based business models, higher score can be achieved when job seeker experienced a major positive change in market share.